
The probability that the bacterium dies between 5 hours and 5.0001 hours should be about 0.0002, and so on.

Then, the probability that the bacterium dies between 5 hours and 5.001 hours should be about 0.002, since this time interval is one-tenth as long as the previous. However, the probability that the bacterium dies between 5 hours and 5.01 hours is quantifiable. A lot of bacteria live for approximately 5 hours, but there is no chance that any given bacterium dies at exactly 5.00. The probability that a bacterium lives exactly 5 hours is equal to zero. Suppose bacteria of a certain species typically live 4 to 6 hours. 10.2 Example: Quotient of two standard normals.10 Products and quotients of independent random variables.8 Function of random variables and change of variables in the probability density function.7 Densities associated with multiple variables.5 Link between discrete and continuous distributions.2 Absolutely continuous univariate distributions.
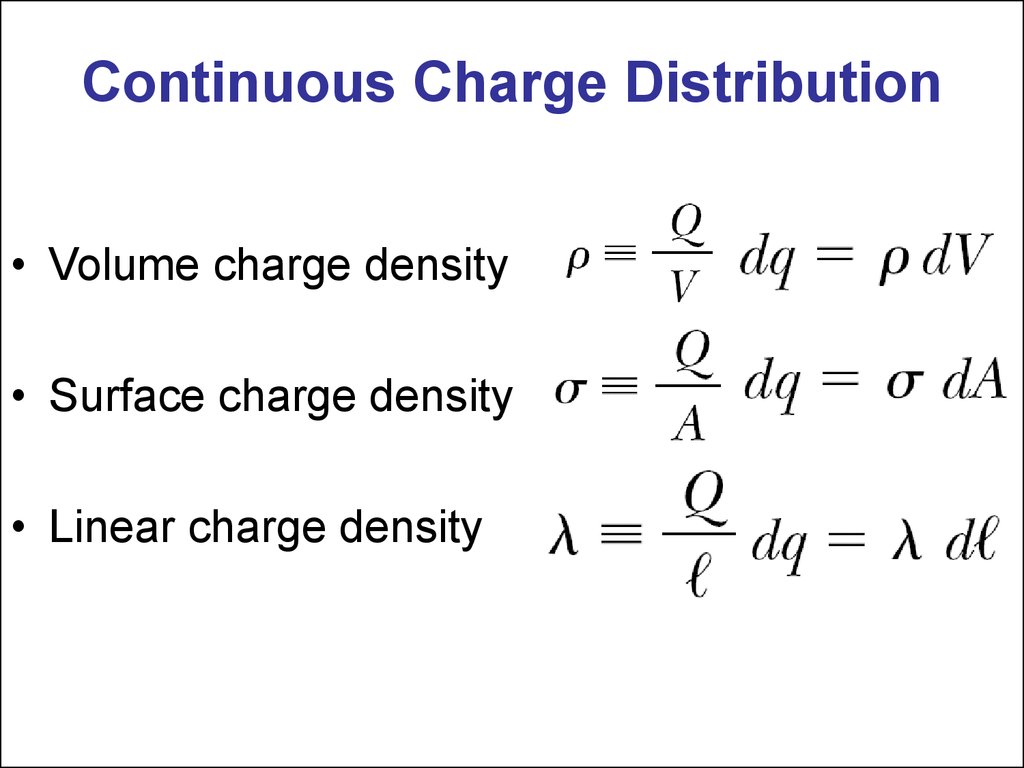
#Formula for density pdf#
In general though, the PMF is used in the context of discrete random variables (random variables that take values on a countable set), while the PDF is used in the context of continuous random variables. "Density function" itself is also used for the probability mass function, leading to further confusion. In other sources, "probability distribution function" may be used when the probability distribution is defined as a function over general sets of values or it may refer to the cumulative distribution function, or it may be a probability mass function (PMF) rather than the density. However, this use is not standard among probabilists and statisticians.
The terms " probability distribution function" and " probability function" have also sometimes been used to denote the probability density function. The probability density function is nonnegative everywhere, and its integral over the entire space is equal to 1. This probability is given by the integral of this variable's PDF over that range-that is, it is given by the area under the density function but above the horizontal axis and between the lowest and greatest values of the range. In a more precise sense, the PDF is used to specify the probability of the random variable falling within a particular range of values, as opposed to taking on any one value. Probability density is the probability per unit length, in other words, while the absolute likelihood for a continuous random variable to take on any particular value is 0 (since there is an infinite set of possible values to begin with), the value of the PDF at two different samples can be used to infer, in any particular draw of the random variable, how much more likely it is that the random variable would be close to one sample compared to the other sample. In probability theory, a probability density function ( PDF), or density of a continuous random variable, is a function whose value at any given sample (or point) in the sample space (the set of possible values taken by the random variable) can be interpreted as providing a relative likelihood that the value of the random variable would be close to that sample.
Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. This article needs additional citations for verification.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
